The most straightforward way to determine interaction partners of a peptide is to use the peptide as bait in affinity pull-down experiments and then by direct detection of binding proteins.
Biotinylated Peptides are designed for screening ELISA (Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) assays that require immobilized peptides onto streptavidin coated 96-well plates, membranes, or glass slides.
Biotinylated peptides containing a specific function domain and corresponding control unmodified peptides, can be immobilized onto beads, which are avidin-conjugated. The beads are then incubated with your target samples. These samples can be a nuclear extract, cell lysates, or purified recombinant protein. After washing steps, the unbound proteins are removed. Bound proteins can then be eluted and analyzed by SDS/PAGE. By comparing proteins bound to modified and unmodified peptides, we can identify the specific function of certain protein.
Applications for Peptide ELISA
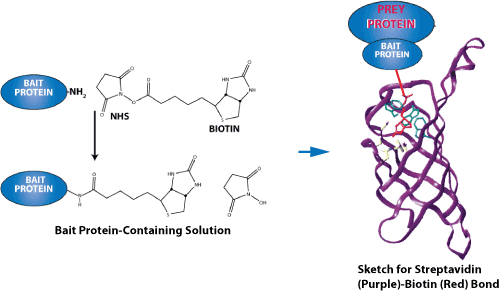
Sketch for streptavidin-biotin bond-force measurements. Because of their exceptionally high binding affinity, two of the most prominent ligand-receptor pairs are streptavidin-biotin and avidin-biotin. Both proteins have a tetrameric structure so that they can bind up to four ligands.
An hsp70 (heat-shock protein of relative molecular mass 70K) can distinguish only unfolded forms of protein. To study the amino acid preferences, Gregory C. Flynn et al. used the random-sequence peptides to fill the binding site of Binding immunoglobulin protein (BiP). It was found that the binding site of BiP shows considerable specificity. The critical residues or Hot spots make a dominant contribution to the free energy of binding. If the key amino acids are mutated, the protein-protein interactions can be disrupted.
Reference:
1. Proximity-dependent labeling identifies dendritic cells that drive the tumor-specific CD4+ T cell response, Science Immunology, 4 Oct 2024, Vol 9, Issue 100, DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.adq8843
2. Nakandakari-Higa S, Walker S, Canesso MCC, et al. Universal recording of immune cell interactions in vivo. Nature. 2024 Mar;627(8003):399-406. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07134-4
3. Lee, C.S., Chen, S., Berry, C.T. et al. Fate induction in CD8 CAR T cells through asymmetric cell division. Nature (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07862-7
4. Pasqual, G., Chudnovskiy, A., Tas, J. et al. Monitoring T cell–dendritic cell interactions in vivo by intercellular enzymatic labelling. Nature 553, 496–500 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25442
5. Gregory C. Flynn, Jan Pohl, Mark T. Flocco & James E. Rothman. Peptide-binding specificity of the molecular chaperone BiP. 24 October 1991, Nature 353, 726-730 doi:10.1038/353726a0.
Please click here for a biotin-labeled peptide synthesis service quote now!