Please click here to get an antibody service quote now!
|
|
||
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a technique to detect the antigen-antibody reaction by the use of enzyme-linked antibodies. ELISA is used mainly to detect and quantify peptides, proteins, or antibodies in a sample. In ELISA, peptide or protein antigens are immobilized on a solid support, either coated directly or through specific capture antibodies. ELISA is based on the use of labelled antibodies so that the resulting conjugates have both immunological and enzymatic activity. The antigen-antibody reaction can be easily measured when adding the reaction substrate.
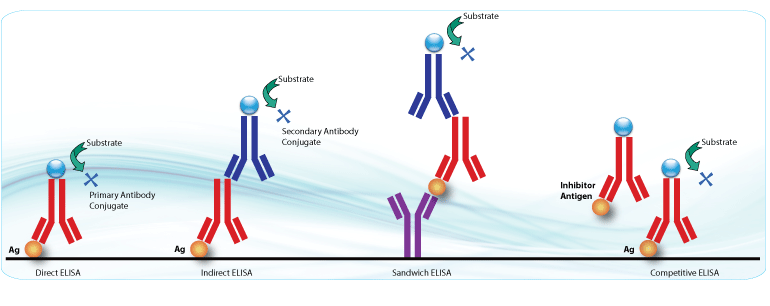
Types of ELISA Methods:
ELISA is a highly sensitive technique and has high specifity. So it is possible to perform population studies in a short time easily and economically. Antigens are immobilized and enzyme-conjugated primary antibodies are used to detect or quantify antigen concentration. This technique has good reproducibility and the results are easy to interpret.
It is the most commonly used method for antibody detection. The coating of the ELISA plate with the antigen against the specific antibodies is needed. The next steps involve the detection with enzyme-conjugated secondary antibodies that recognize the primary antibodies. In this way, the primary antibodies have their maximum immunoreactivity, while the secondary antibodies are capable of signal amplification.
This is the most frequent ELISA for antigen detection. The plates are usually coated with an antibody (monoclonal or polyclonal antibody) against the unknown antigen. The antigen to be detected is between a layer of capture antibodies and a layer of detection antibodies. The method requires that antigens have at least two antibody binding sites to prevent cross-reactivity or competition of binding sites.
This technique is also very common for the detection of specific antibodies. The antigen of interest from crude or impure samples and immobilized known antigen compete for binding to the capture antibody.
The Sandwich Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) measures the amount of antigen between two layers of antibodies. It is a sensitive and robust method to measure the antigen concentration in an unknown sample. The antigen to be measured must contain at least two antigenic sites capable of binding to two antibodies: the capture and the detection antibodies.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quote or order now. We'll process your order immediately. Or CLICK HERE for the quotation form.
Please click here to get an antibody service quote now!