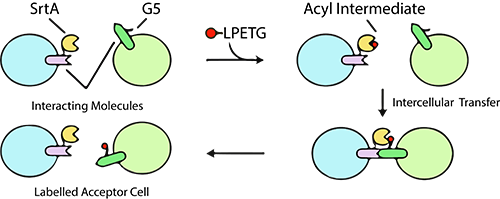
| 
Significance and functions of the LPETGS motif:
- Protein Targeting: The LPETGS motif serves as a signal sequence that directs proteins to specific cellular organelles. For example, it is recognized by the signal recognition particle (SRP) during the cotranslational targeting of proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum, where they are synthesized and folded.
- ER Localization: Proteins containing the LPETGS motif are often translocated into the endoplasmic reticulum, a crucial organelle involved in protein synthesis, modification, and quality control. This motif aids in the proper localization of these proteins within the ER.
- Mitochondrial Targeting: In some cases, the LPETGS motif is involved in the targeting of proteins to the mitochondria, which are responsible for energy production within the cell. This motif plays a role in ensuring that the proteins are directed to the mitochondrial outer membrane.
- Protein Folding and Quality Control: Proteins that contain the LPETGS motif may undergo specific folding and quality control processes within the ER. This helps ensure that only properly folded and functional proteins are allowed to exit the ER and reach their final cellular destinations.
- Biomedical Implications: Understanding the LPETGS motif's role in protein targeting and localization is of great significance in biomedical research. Researchers study this motif to gain insights into various diseases and conditions where protein trafficking and localization are disrupted, such as certain types of congenital disorders and neurodegenerative diseases.
|
 https://www.lifetein.com
100 Randolph Road, Suite 2D,
Somerset
USA
New Jersey
08873
https://www.lifetein.com
100 Randolph Road, Suite 2D,
Somerset
USA
New Jersey
08873
 https://www.lifetein.com
100 Randolph Road, Suite 2D,
Somerset
USA
New Jersey
08873
https://www.lifetein.com
100 Randolph Road, Suite 2D,
Somerset
USA
New Jersey
08873