Click chemistry, a groundbreaking technique recognized by the 2022 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, has revolutionized peptide synthesis. Developed by Carolyn R. Bertozzi, Morten Meldal, and K. Barry Sharpless, this method enables efficient and precise conjugation of peptides with other biomolecules. At the forefront of this innovation, LifeTein leverages click chemistry to create peptide-drug conjugates with remarkable applications.
Key Takeaways
- Click Chemistry Defined: Click chemistry involves the selective and irreversible coupling of two molecular components. In peptide synthesis, this technique allows for precise and efficient conjugation.
- Cu (I)-Catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Click Chemistry (CuAAC): LifeTein employs CuAAC to link peptides with azide and alkyne functional groups. This robust reaction enables the creation of peptide-drug conjugates.
- Strain-Promoted Azide-Alkyne Click Chemistry (SPAAC): SPAAC, a copper-free variant, facilitates bioconjugation without the need for metal catalysts.
- Tetrazine-Alkene Ligation: LifeTein also utilizes tetrazine-alkene ligation, a powerful click chemistry approach, for peptide-drug conjugation.
Applications
- Peptide-Drug Conjugation: LifeTein’s expertise extends to developing peptide-drug and antibody-drug conjugates. Successful conjugations involve drugs like MMAE, Panobinostat, Tazmetostat, and FK506.
- Site-Specific PEGylation: Using maleimide or click chemistry, LifeTein achieves site-specific PEGylation of peptides. These PEGylated peptides find applications in various fields.
- Photo Crosslinking Peptides: Incorporating photo-labile amino acids, such as p-benzoyl-L-phenylalanine (Bpa), LifeTein enables downstream click chemistry. Functionalized alkynes, fluorophores, and other groups can be efficiently linked to peptides.
Explore LifeTein’s Custom Synthesis Services
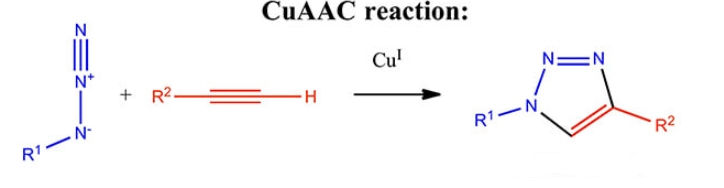
Mechanisms of Click Chemistry
Cu (I)-Catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Click Chemistry (CuAAC)
CuAAC, also known as the Huisgen reaction, remains a cornerstone in peptide synthesis. Here’s how it works:
- Azide and Alkyne Functionalization: Peptides are modified with azide (–N₃) and alkyne (–C≡CH) groups.
- Copper(I) Catalyst: In the presence of a copper(I) catalyst, the azide and alkyne react to form a stable triazole linkage.
- High Yield and Selectivity: CuAAC offers excellent yield and selectivity, making it ideal for peptide conjugation.
Strain-Promoted Azide-Alkyne Click Chemistry (SPAAC)
SPAAC, a copper-free variant, avoids the need for metal catalysts. Key features:
- Strain-Driven Reaction: The reaction relies on strained cyclooctynes (e.g., DBCO) and azides. No copper required!
- Bioorthogonal: SPAAC occurs selectively in biological environments without interfering with native biomolecules.
Tetrazine-Alkene Ligation
LifeTein also employs tetrazine-alkene ligation for peptide-drug conjugation:
- Tetrazine and Alkene: Peptides are functionalized with tetrazine and alkene groups.
- Rapid Reaction: Tetrazine reacts with alkene (e.g., trans-cyclooctene) in a bioorthogonal, rapid ligation.
FAQ
Q: What advantages does click chemistry offer in peptide synthesis?
A: Click chemistry provides precise, efficient conjugation, enabling the creation of peptide-drug conjugates and other bioconjugates.
Q: Which drugs are successfully conjugated by LifeTein?
A: LifeTein excels in conjugating MMAE, Panobinostat, Tazmetostat, and FK506 to peptides.
Q: Can LifeTein perform site-specific PEGylation of peptides?
A: Yes! Using maleimide or click chemistry, LifeTein achieves site-specific PEGylation for versatile applications.


