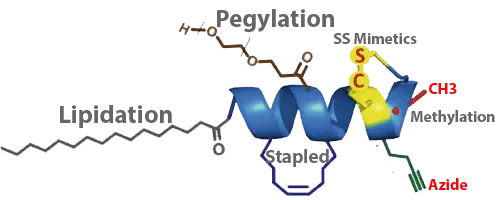
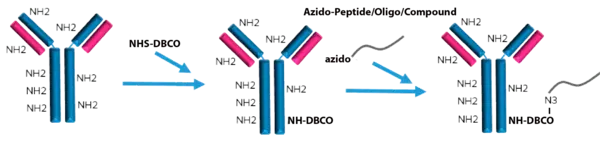Peptide Modifications
LifeTein provides a wide range of peptide modification services and biomolecule peptide conjugation services.
Peptide chemistry toolbox for peptide therapeutics: modifications of the peptide backbone, lipidation, attaching polymers or modulating the primary, secondary, tertiary or quaternary structure.
Peptide Antibody Conjugation Service:
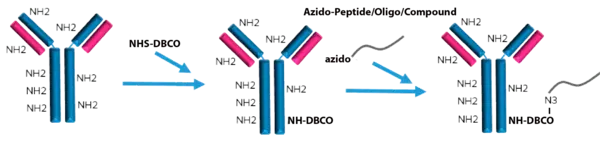
LifeTein provides peptide-macromolecule bioconjugation service. The service allows for the conjugation of oligonucleotides, fluorescent dyes, chromogenic enzyme substrates, drugs, toxins, or carrier proteins to the peptides. The peptide can be conjugated to the molecules through the chemical reactive groups such as amine, thiol, or carboxylate.
Val-Cit-PAB-MMAE (CAS # 646502-53-6, Molecular Formula: C68H105N11O15, Molecular Weight: 1316.63) is a precursor of antibody drug conjugate. It contains a maleimidocaproyl (MC) spacer, a protease-sensitive Val-Cit dipeptide, a PABC linker and a MMAE payload. MC-Val-Cit-PAB-MMAE, or Maleimidocaproyl-valine-citrulline-p-aminobenzoyloxycarbonyl-monomethyl auristatin E, can be attached to any peptides.
LifeTein's service portfolio includes peptide oligo conjugates for gene inhibition, siRNA delivery, cellular entry, protein to protein interaction, nucleic acid-protein interaction, or drug delivery; peptide antibody conjugates for drug therapy, diagnostics and microarray detection, or therapeutic drug discovery; biotin peptide conjugates for immunoassay, or pull down assay; and synthetic polymers for pegylation, dendrimers, nanoparticles, or gold particles.
LifeTein Click Chemistry Features and Benefits:
- Stable - forms a triazole
- Biocompatible - occurs efficiently under mild conditions; requires no accessory reagents such as a copper catalyst or reducing agents (e.g. Cu(I), DTT)
- Chemoselective - no reactions to -NH2, -SH, -COOH or other protein functionalities or active groups
- Effective - All reactions are in aqueous media, yielding high conjugation efficiency
- Flexible - 4 carbon atom spacer or choice of longer arm keeps molecules close
Applications
- Oligo peptide conjugates: DNA conjugates, RNA conjugates, siRNA conjugates
- Peptide-Antibody Conjugation
- Dendritic Peptide
- Peptide-Drug Conjugates
- Peptide-Protein Conjugation
- Peptide-small molecule Conjugation
Click here to download the LifeTein Peptide Modification Full List
N Terminus
- {Ac},Acetylation (Free) Increase the metabolic stability, enhances the peptide activity.
- {For}, Formylation: Lysine formylation can arise from oxidative damage of DNA. This modification may be involved in development of diseases linked to this stress, including cancer.
- {Fmoc}, 9-Fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl: Fmoc is a base-labile protecting group used in organic synthesis.
- {Suc}, succinyl;{MeO-Suc}: Succinylation (-CO-CH2-CH2-CO-) is a posttranslational modification where a succinyl group is added to a lysine residue of a protein molecule. Lysine Succinylation Is a Frequently Occurring Modification in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes and Extensively Overlaps with Acetylation.
- {Cl-Ac}, Chloroacetyl: The univalent carboacyl group formed by loss of -OH from the carboxy group of chloroacetic acid.
- {Mal}, Maleimide: The maleimide has the fast reaction rates and significantly high selectivity towards cysteine residues in proteins. A large variety of maleimide heterobifunctional reagents are used for the preparation of targeted drug therapies such as the antibody-drug conjugates.
- {CBZ}, Benzyloxycarbonyl: The carboxybenzyl group (Cbz) is commonly used in organic synthesis as a protecting group for amines.
- {Br-Ac}, Bromoacetyl: It is shown that bromoacetyl bromide can be utilized for the selective cleavage of ethers and acetals in high yields.
- Nitrilotriacetyl: It is used as a chelating agent.
- {Boc}, tertbutoxycarbonyl: The BOC group can be added to the amine under aqueous conditions. Removal of the BOC in amino acids can be accomplished with strong acids such as trifluoroacetic acid.
- {HPP}, 4-Hydroxyphenylpropionic acid: It has antioxidants properties and is actively absorbed by the monocarboxylic acid transporter. Replacement of the Tyr hydroxyl group in opioid peptides with a carbamoyl (-CONH) group resulted in compounds that retained high opioid agonist potency. This is due to additional hydrophobic binding interactions of the two methyl groups with the receptor. This can be done by adding the HPP group to the peptide.
- {LA}, Lipoic acid: Alpha lipoic acid is a low molecular weight dithiol antioxidant. The lipoic acid modified peptide is used for Anti Wrinkle Skin Care, diabetic study and a beneficial therapeutic agent to chelate metal ions, repair oxidized proteins, regulate gene transcription, and inhibit the activation of NK-κB.
- {mPEG2000}, {mPEG3000}, {mPEG5000}, Mal-PEG12: Polyethyleneglycol is an amphiphilic polymer consisting of repeating units of ethylene oxide. PEG is a biologically inert, non-immnunogenic linear polyether diol. It is being used to enhance water solubility, reduce immunogenicity, increase in vivo circulation half-life by preventing enzymatic degradation, prolong the in vivo action, accelerate targeting drug delivery. The PEGylation of peptide shows improvement of bioavailability of drugs, in particular enzyme inhibitors, or creation of polymers with encapsulating properties for drugs. LifeTein’s Click-PEGylation, the thiol labelling step via a click chemistry conjugation reaction, gives improved flexibility to peptides.
- {Alloc}, allyloxycarbonyl
- {Boc}, tertbutoxycarbonyl
- {But}, Butyric acid
- {Hex}, Hexanoic acid
- {Oct}, Octanoic acid
- {Dec}, Decanoic acid
- Fatty acid: Peptide conjugated with fatty acid can be used to prolong the half-life in the circulation significantly, increase the cell penetration, or antibacterial activity. The commonly used fatty acids are Caprylic acid (C8), Capric acid (C10), Lauric acid (C12), Myristic acid (C14), Palmitic acid (C16) or Stearic acid (C18). Modifying peptides with fatty acids can substantially improve their pharmacokinetic properties. Liraglutide, a peptide drug for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, has a fatty acid attached, extending the half-life of 11–15 hours.
- Caprylic acid: The octanoyl moiety is crucial for the peptide hormone Ghrelin. The Octanoylated ghrelin regulates the secretion of the growth hormone.
- {Pal}, Palmitic acid: Palmitic acid conjugated peptides increase the cell permeability and help binding of the peptides to cell membrane. The lipid conjugation of a peptide antigen increases affinity of binding to MHC class II and T-cell receptor. Albumin-binding achieved by fatty-acylation to drugs is considered to be an effective means of prolonging the circulation lifetimes of short-lived peptides. For example, palmitic acid-conjugated exendin-4, a potential anti-diabetic drug, has a delayed absorption and prolonged circulation for longer hypoglycemia.
- {Ste}, Stearic acid: The stearic acid-modified peptide improves pharmacokinetic properties and anticoagulant activity. The Stearic acid modified peptide is resistance to degradation mediated by thrombin and trypsin and shows a significantly increased half-life.
- {Myr}, Myristic acid: The myristoyl moiety can mediate protein subcellular localization, protein-protein interaction or protein-membrane interactions. The myristoylation is one of the regulators of cellular bioactive lipid concentration.
- {Lau}, Lauric acid: CGKRK is a well-known tumor targeting peptide. The lauric acid modified peptide enhances cellular permeation and delivery of siRNA targeted to tumor cells for effective silencing of selected proteins. The conjugation of fatty acids to CGKRK could create an efficient delivery system for siRNA silencing specifically in tumor cells.
- More...
1. Short-Chain Fatty Acids (Usually fewer than 6 carbon atoms)
| Name |
Carbon Atoms |
Formula |
Saturation |
| Formic acid |
C1 |
HCOOH |
Saturated |
| Acetic acid |
C2 |
CH₃COOH |
Saturated |
| Propionic acid |
C3 |
CH₃CH₂COOH |
Saturated |
| Butyric acid |
C4 |
CH₃(CH₂)₂COOH |
Saturated |
| Valeric acid |
C5 |
CH₃(CH₂)₃COOH |
Saturated |
2. Medium-Chain Fatty Acids (6 to 12 carbon atoms)
| Name |
Carbon Atoms |
Formula |
Saturation |
| Caproic acid |
C6 |
CH₃(CH₂)₄COOH |
Saturated |
| Caprylic acid |
C8 |
CH₃(CH₂)₆COOH |
Saturated |
| Capric acid |
C10 |
CH₃(CH₂)₈COOH |
Saturated |
| Lauric acid |
C12 |
CH₃(CH₂)₁₀COOH |
Saturated |
3. Long-Chain Fatty Acids (13 to 21 carbon atoms)
| Name |
Carbon Atoms |
Formula |
Saturation |
| Myristic acid |
C14 |
CH₃(CH₂)₁₂COOH |
Saturated |
| Palmitic acid |
C16 |
CH₃(CH₂)₁₄COOH |
Saturated |
| Stearic acid |
C18 |
CH₃(CH₂)₁₆COOH |
Saturated |
| Oleic acid |
C18:1 |
CH₃(CH₂)₇CH=CH(CH₂)₇COOH |
Monounsaturated |
| Linoleic acid |
C18:2 |
CH₃(CH₂)₄(CH=CHCH₂)₂(CH₂)₆COOH |
Polyunsaturated |
| Arachidic acid |
C20 |
CH₃(CH₂)₁₈COOH |
Saturated |
4. Very-Long-Chain Fatty Acids (22 or more carbon atoms)
| Name |
Carbon Atoms |
Formula |
Saturation |
| Behenic acid |
C22 |
CH₃(CH₂)₂₀COOH |
Saturated |
| Lignoceric acid |
C24 |
CH₃(CH₂)₂₂COOH |
Saturated |
| Cerotic acid |
C26 |
CH₃(CH₂)₂₄COOH |
Saturated |
C Terminus
- {NH2}, Amidation (Free)
- {CHO}, Peptide Aldehydes
- {OL}, Alcohol Peptide
- {CMK}, Chloromethylketone
- {AMC}, 7-Amino-4-Methylcoumarin
- {pNA},p-Nitroaniline
- {-ONP}, para-nitrophenol
- {-OSu}, hydroxysucinimide ester
- ED, {AFC}, -OMe, -OtBu
- {FMK}, Fluoromethylketone
- {Cya}, Cysteamide
- More...
D Amino Acid
- {D-Ala}
- {D-Arg}
- {D-Asp}
- {D-Asn}
- {D-Cys}
- {D-Glu}
- {D-Gln}
- {D-His}
- {D-Allo-Ile}
- {D-Leu}
- {D-Lys}
- {D-Met}
- {D-Pro}
- {D-Phe}
- {D-Ser}
- {D-Tyr}
- {D-Thr}
- {D-Trp}
- {D-Val}
- More...
Special Amino Acids
- {Cys(Cam)}
- {D-Cys(Cam)
- {Cys(Acm)}
- {Cys(tBu)}
- {Cys(StBu)}
- {Cys(Nitrosothiols)}
- {Cys(Pyrene-Maleimide)}
- {Gamma-Glu}
- {D-Gamma-Glu}
- {Beta-Asp}
- {D-Beta-Asp}
- {Met(O)}
- {D-Met(O)}
- {Lys(Ac)}
- {Ac-Lys}
- {Lys(Dde)}
- {Gly(allyl)}
- {D-Gly(allyl)}
- {Cpg}, Cyclopentylglycine
- {Tle}
- {Ser(Octanoic acid)}
- {Ser(Lipoic acid)}
- {D-Ser(Octanoic acid)}
- {3-Ala(2-thienyl)-OH}
- {3-Ala(3-thienyl)-OH}
- {Aib}
- {Abu}
- {D-Abu}
- {Hyp}
- {Phg}
- {D-Phg}
- {Nva}
- {D-Nva}
- {Nle}
- {D-Nle}
- {Cit}
- {D-Cit}
- {Orn}
- {D-Orn}
- {Pen}
- {D-Pen}
- {Cha}
- {D-Cha}
- {Chg}
- {D-Chg}
- {Dab}
- {Dap}
- {Pra}
- {D-Pra}
- {Allo-Thr}
- {D-Allo-Thr}
- More...
Fluorescent Labeling
- Cyanine 3, Cyanine 5, Cyanine 5.5, Cyanine 7, Cyanine 7.5, BDP 581/591, cy3, cy5, Texas Red, More details
- Alexa Fluor 350, Alexa Fluor 405, Alexa Fluor 488, Alexa Fluor 532, Alexa Fluor 546, Alexa Fluor 555, Alexa Fluor 568, Alexa Fluor 594, Alexa Fluor 647, Alexa Fluor 680, Alexa Fluor 750
- Qdot 525, Qdot 565, Qdot 605, Qdot 655, Qdot 705, Qdot 800
- Biotin (N terminus)
- DeThioBiotin
- EDBiotin (C terminus)
- Lys(Biotin) (middle)
- Lys(Biotin) (C terminus)
- Lys(LC-Biotin) (middle)
- Lys(LC-Biotin) (C terminus)
- Lys(Biotin) (N terminus)
- Biotin-LC (N terminus)
- FITC (N terminus)
- Lys(FITC) (middle)
- Lys(FITC) (C terminus)
- Lys(FITC) (N terminus)
- FITC-LC (N terminus)
- 5-FAM (N terminus)
- 6-FAM (N terminus)
- Lys(5-FAM) (middle)
- Lys(5,6-FAM)
- Lys(5-FAM) (C terminus)
- Lys(5-FAM) (N terminus)
- 5-FAM-LC (N terminus)
- Dansyl (N terminus)
- EDDansyl (C terminus)
- Lys(Dansyl) (middle)
- Lys(Dansyl) (C terminus)
- Lys(Dansyl) (N terminus)
- Dansyl-LC (N terminus)
- TAMRA (N terminus)
- 5(6)-TAMTA-
- EDTAMRA (C terminus)
- Lys(TAMRA) (middle)
- Lys(TAMRA) (C terminus)
- Lys(TAMRA) (N terminus)
- TAMRA-LC (N terminus)
- Lys(Dnp) (middle)
- D-Lys(Dnp) (middle)
- Dab(Dnp) (middle)
- Dap(Dnp) (middle)
- EDDnp (C terminus)
- MCA (N terminus)
- Lys(MCA) (middle)
- Lys(MCA) (C terminus)
- Lys(MCA) (N terminus)
- 3-Indolylacetic acid (N terminus)
- Cys(Npys) (N terminus)
- PyBA- (N terminus), 1-pyrenebutyric acid
- Lys(PyBA)
- Fa- (N terminus), 3-[2-2furyl]acrylic acid
- Rhodamine B- (N terminus)
- Lys(Rhodamine B)
- More...
Spacers and Linkers
- {Gly}, 2 Carbons
- {Beta-Ala}, 3 Carbons
- {GABA}, 4 Carbons
- {Ava}, 5 Carbons
- {Ahx}, 6 Carbons
- {AEA},Aminoethoxyacetic Acid
- {Mini-PEG}, 9 Carbons
- {Mini-PEG2}, 13 Carbons
- {Mini-PEG3}, 16 Carbons
- {ANP Linker}
- More details
N-Methyl Amino Acids
Post-translational modifications of histone proteins, such as acetylation, methylation, and phosphorylation, play essential roles in regulating chromatin dynamics. The mono-, di-, or tri-methylated peptides can be used to study the protein-protein interactions. In a new study, an H3 histone tail mimicking peptides were used to bind with the ASHHH2 CW domain.The monomethylated ARTK(me1)QTARY, dimethylated ARTK(me2)QTARY, and trimethylated ART- K(me3)QTARY were synthesized by LifeTein
(95% purity by mass spectrometry).
Reference: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12104-018-9811-x
The methylated peptide is an important tool to study the histone methylation. Histone methylation can be associated with either transcriptional repression or activation. There is an emerging realization that DNA and histone lysine methylation in mammals are highly interrelated. Targeting of DNA methylation is mechanistically linked to H3K9 methylation. For example, the p53 gene is the most frequently mutated tumor suppressor gene in human cancers. Upon genotoxic stresses, p53 proteins are activated in the setting of multiple post-translational modifications such as phosphorylation, methylation and acetylation for full activation.
- {Cys(Me)}, SMC
- {ADMA}, {Arg(Me)2} asymmetrical
- {SDMA}, {Arg(Me)2} symmetrical
- {Arg(Me)}
- {Thr(Me)}
- {Ser(Me)}
- {Lys(Me)}
- {Lys(Me2)}
- {Lys(Me3)}
- {L-1-Me-Trp}
- {L-2-Me-Trp}
- {D-2-Me-Trp}
- {Tyr(Me)}
- {Tyr(Et)}
- {D-Tyr(Et)}
- {Orn(Me)3}
- {N-Me-Gly}, Sar
- {N-Me-Ser}
- {N-Me-Tyr}
- {N-Me-Thr}
- {N-Me-Asp}
- {N-Me-Glu}
- {N-Me-Ala}
- {N-Me-Phe}
- {N-Me-Leu}
- {N-Me-Ile}
- {N-Me-Val}
- {N-Me-Met}
- {N-Me-Nle}
- {N-Me-Nva}
- More...
Phosphorylation (pSer, pTyr, or pThr)
- {pSer}
- {D-pSer}
- {pTyr}
- {D-pTyr}
- {pThr}
- {D-pThr}
- 2, 3 or 4 phosphorylation sites in the sequence
- More...
Other Modifications and Free Services
- Up to 10 Free Aliquots (Why Aliquot?)
- Free HPLC Data
- Free MS Data
- Free Certificate Of Analysis (COA)
- Convert from TFA Salt to Acetate Salt or Hydrochloride Salt
- Amino Acid Analysis
- N Elemental Analysis
- Solubility Test
- Bioburden
- Water Content
- Bacterial Endotoxins
- More...