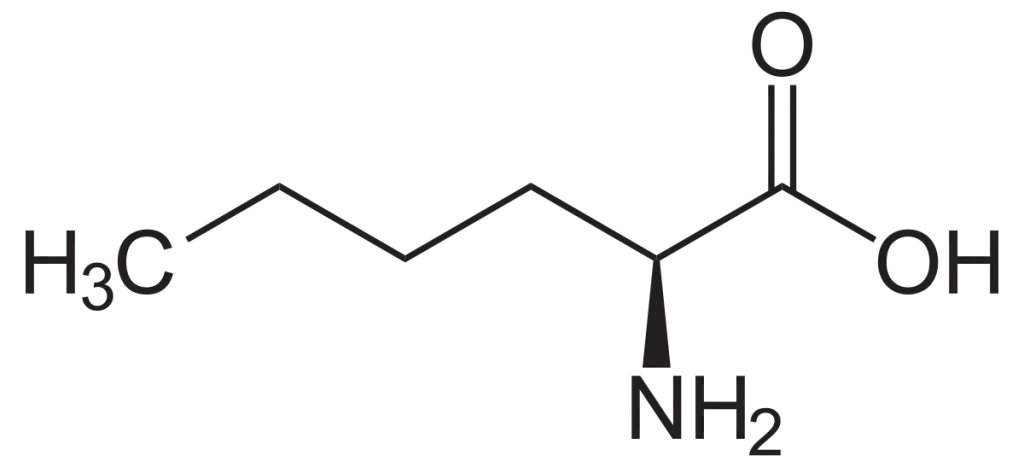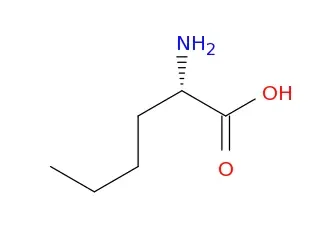
Fluorescent labeling is a crucial technique in molecular biology, allowing researchers to visualize and track biological molecules. Among the various fluorescent dyes available, Cy3 (Cyanine3) stands out due to its bright orange fluorescence and versatility. This article explores the properties, applications, and synthesis of Cy3, with insights from LifeTein’s expertise in fluorescent labeling.
Key Takeaways
- Bright Orange Fluorescence: Cy3 is a bright, orange-fluorescent dye used for labeling proteins and nucleic acids.
- Excitation and Emission: Excited at 550 nm, emits at 570 nm.
- Applications: Widely used in immunocytochemistry, flow cytometry, and genomics.
- LifeTein Expertise: LifeTein offers Cy3 labeling services for custom peptide synthesis.
Properties of Cy3
Bright Orange Fluorescence
Cy3 is a bright, orange-fluorescent dye that is widely used for labeling proteins and nucleic acids. Its fluorescence properties make it an excellent choice for various imaging techniques.
Excitation and Emission
Cy3 has an excitation maximum at 550 nm and an emission maximum at 570 nm, making it compatible with common fluorescence microscopy setups. This allows for easy detection and imaging of labeled molecules.
Chemical Stability
Cy3 is chemically stable and can be conjugated to various biomolecules without significant loss of fluorescence. This stability is essential for long-term imaging and tracking experiments.
Applications of Cy3
Immunocytochemistry
Cy3 is extensively used in immunocytochemistry to label antibodies. By conjugating Cy3 to antibodies, researchers can visualize the location and distribution of target proteins within cells.
Flow Cytometry
In flow cytometry, Cy3-labeled antibodies are used to analyze and sort cells based on the presence of specific proteins. This technique is valuable for studying cell populations and identifying biomarkers.
Genomics
Cy3 is also employed in genomics research for labeling nucleic acids. It is used in techniques such as fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) to detect specific DNA sequences within cells.
Custom Peptide Synthesis
LifeTein offers custom peptide synthesis services, including Cy3 labeling. Researchers can request Cy3-labeled peptides for their specific applications, ensuring high-quality and consistent results3.
Find more labelling options here.
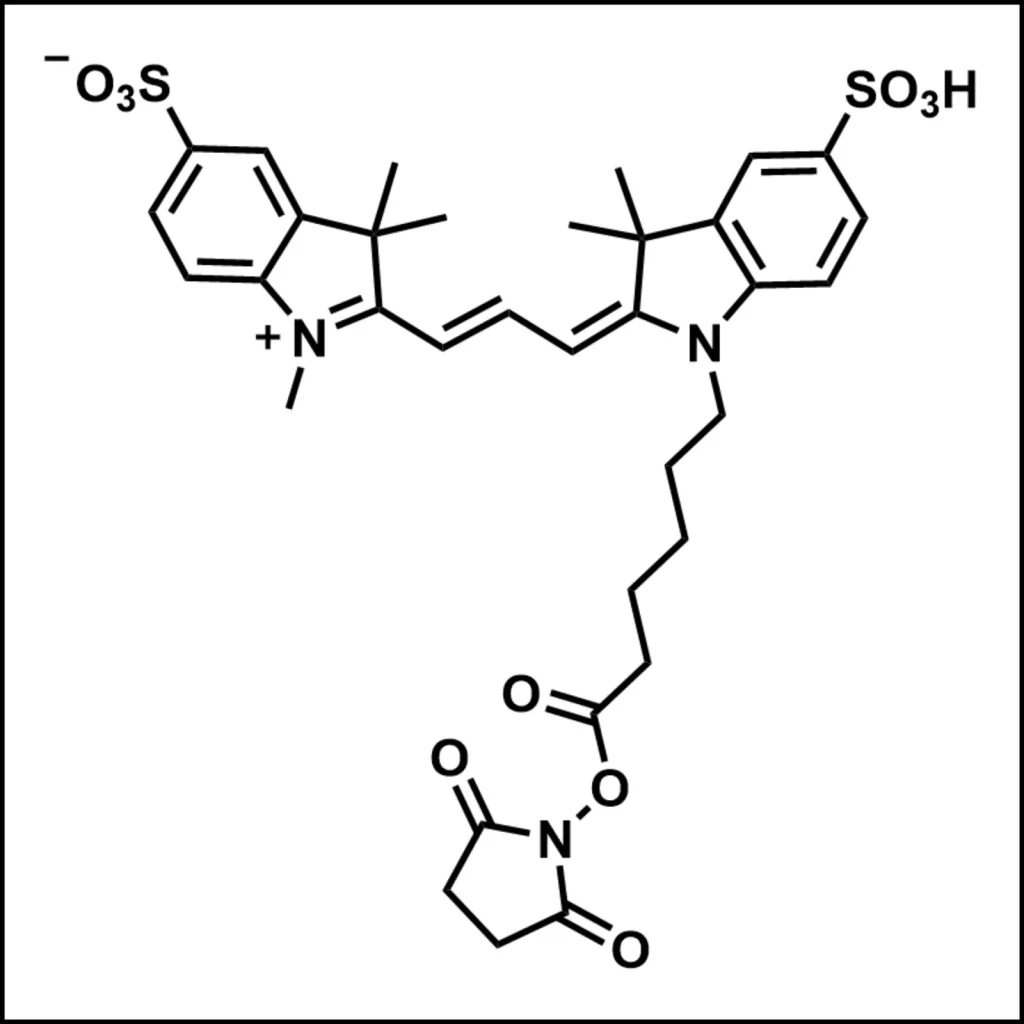
Synthesis of Cy3-Labeled Molecules
Conjugation to Proteins
Cy3 can be conjugated to proteins through amine-reactive NHS-esters, which react with primary amines on the protein surface. This reaction forms a stable covalent bond, ensuring that the dye remains attached during imaging.
Conjugation to Nucleic Acids
For nucleic acids, Cy3 can be conjugated to the 5′ end of DNA or RNA molecules. This labeling allows for the visualization of specific nucleic acid sequences within cells or tissues.
Optimization of Labeling Conditions
Optimizing the labeling conditions, such as pH and reaction time, is crucial for achieving high labeling efficiency and maintaining the biological activity of the labeled molecules.
Future Directions
Advancements in Fluorescent Labeling
Ongoing research aims to develop new fluorescent dyes with improved properties, such as higher brightness, photostability, and reduced background fluorescence. These advancements will enhance the sensitivity and accuracy of fluorescent labeling techniques.
Expanding Applications
As the technology advances, the applications of fluorescent labeling with Cy3 and other dyes are expected to expand into new areas, including targeted drug delivery, biosensors, and live-cell imaging.
Find more peptide synthesis options here.
FAQ
What Is Cy3?
Cy3 is a bright, orange-fluorescent dye used for labeling proteins and nucleic acids.
Why Is Cy3 Important?
Cy3 is valuable for its bright fluorescence, compatibility with common imaging techniques, and wide range of applications in molecular biology.
How Is Cy3 Synthesized?
Cy3 can be synthesized chemically and then conjugated to biomolecules through amine-reactive NHS-esters or other reactive groups.
What Services Does LifeTein Offer?
LifeTein provides custom peptide synthesis services, including Cy3 labeling, to meet the specific needs of researchers.