Please click here for the full article: Peptide Antigen Design: Best Practices: https://www.lifetein.com/peptide-antigen-design.html
Homology Considerations:
Two basic strategies can be used to address peptide antigen design. Both approaches should be considered when analyzing the protein sequence.
- A unique sequence or region should be selected to ensure the specificity of the target protein.
- A homologous sequence should be chosen so that a single antibody can recognize multiple proteins.
Epitope Selection:
Continuous Epitopes, Discontinuous Epitopes:

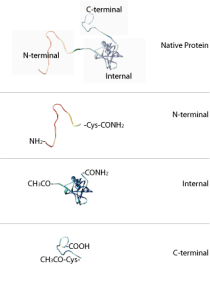
Targeting the N-terminus or C-terminus:
Sequence Length:
Peptide Purity:
Peptide Solubility
Amino acid classifications
Hydrophobic (non-polar) amino acids: Ala, Ile, Leu, Met, Phe, Trp, Val
Uncharged (polar) amino acids: Asn, Cys, Gly, Gln, Pro, Ser, Thr, Tyr
Acidic (polar) amino acids: Asp, Glu
Basic (polar) amino acids: His, Lys, Arg
Difficult Amino Acids
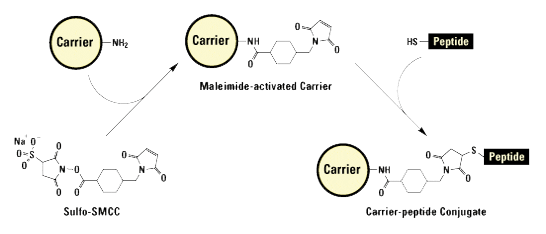
Carrier Protein Coupling Considerations:
Common carrier proteins used for antibody production:
Multiple antigenic peptides (MAPs)
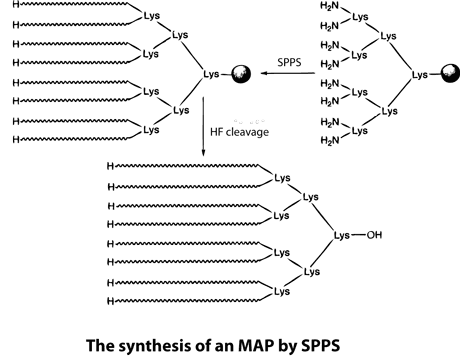
Peptide Modifications
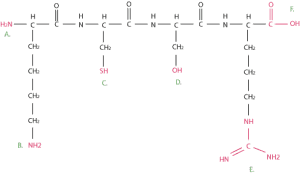
A. N-terminal amino group
B. C-terminal carboxyl group
C. alpha-Amino group on lysine
D. Hydroxyl group on serine, threonine, and tyrosine
E. Guanidine group on arginine
F. Thiol group on cysteine