Fluorescent Labeling with Abz, where Abz stands for 2-aminobenzoyl, is an indispensable technique in biochemical and pharmacological research, particularly for studying enzyme kinetics and protein interactions. As a highly efficient fluorescent donor, Abz is renowned for its optimal spectral properties, including significant Stokes shift and high quantum yield, which facilitate sensitive detection in complex biological matrices. Its primary utility lies in Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET)-based assays, where it is paired with quenchers like 3-nitro-tyrosine (Tyr(NO2)) or 2,4-dinitrophenyl (Dnp) to create sensitive substrates for proteolytic enzymes. Consequently, this powerful labeling strategy enables real-time monitoring of protease activity, precise determination of kinetic parameters, and high-throughput screening of potential therapeutic inhibitors.
Key Takeaways
- Abz is an excellent fluorescent donor in FRET systems owing to its favorable photophysical properties, including a high quantum yield and a favorable Stokes shift.
- It is most commonly used in donor-quencher pairs (e.g., Abz/Dnp or Abz/Tyr(NO2)) to create fluorogenic substrates for monitoring protease activity.
- Fluorescence quenching in these substrates is relieved upon enzymatic cleavage, generating a measurable increase in fluorescence intensity.
- Abz-labeled peptides are crucial tools for studying enzymes like ACE (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme) and various matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs).
- The site-specific incorporation of Abz during solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) allows for the custom design of sensitive and specific assay probes.
Fundamentals of the Abz Fluorophore
Chemical Structure and Spectral Properties
The 2-aminobenzoyl (Abz) group is a derivative of anthranilic acid. Its structure features an aromatic benzene ring coupled with an electron-donating amino group, which is responsible for its strong fluorescence. Abz is typically excited in the near-ultraviolet to blue region, with a maximum absorbance around 320 nm, and emits blue fluorescence with a peak around 420 nm. This separation between excitation and emission wavelengths, known as the Stokes shift, is advantageous as it minimizes interference from scattered excitation light, thereby enhancing signal-to-noise ratios in assays.
The Principle of FRET and Quenching
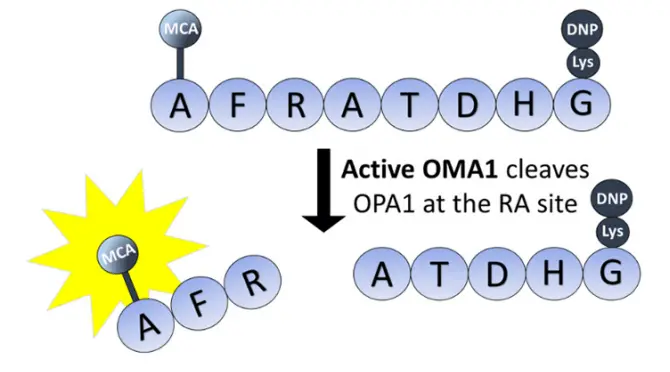
The exceptional utility of Abz arises from its role in fluorescence quenching mechanisms. In a typical application, the Abz fluorophore is chemically incorporated into a peptide sequence at one site, while a suitable quencher molecule is attached at another. When in close proximity, the energy from the excited Abz is non-radiatively transferred to the quencher, resulting in low background fluorescence. This intact, quenched molecule serves as a fluorogenic substrate. Upon cleavage by a specific protease at the site between the donor and quencher, the physical separation disrupts the energy transfer. This disruption leads to a dramatic increase, often a 20 to 30-fold enhancement, in Abz fluorescence, which can be monitored in real-time.
Find out more about fluorescent peptides here.
Primary Applications in Biomedical Research
Monitoring Protease Activity and Kinetics
Abz-based fluorogenic substrates are a gold standard for studying proteolytic enzymes. The design is versatile: a target protease’s cleavage sequence is flanked by the Abz donor and an appropriate quencher. For example, substrates like Abz-FRK(Dnp)P-OH are specifically designed for the enzyme ACE (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme), a key target in hypertension and heart failure research. The real-time increase in fluorescence directly correlates with enzyme activity, allowing researchers to calculate critical kinetic parameters, such as the Michaelis constant (Km) and the catalytic rate constant (kcat), with high precision and sensitivity.
High-Throughput Drug Screening
The sensitivity and adaptability of Abz-based assays make them ideal for high-throughput screening (HTS) platforms in drug discovery. Pharmaceutical companies and research laboratories routinely use these substrates to screen vast chemical libraries for potential inhibitors of disease-relevant proteases. Targets include renin (involved in blood pressure regulation), beta-secretase (BACE-1) (implicated in Alzheimer’s disease), and various cathepsins and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) associated with cancer metastasis and inflammatory diseases. The homogeneous, “mix-and-read” format of these assays significantly accelerates the discovery of lead compounds.
Investigating Protein-Protein Interactions
Beyond simple cleavage assays, the Abz fluorophore can be used in more sophisticated FRET-based binding studies. In this context, Abz is attached to one protein, while a compatible acceptor fluorophore (not a quencher) is attached to its binding partner. A change in FRET efficiency signals a binding event or a conformational change. This application is powerful for characterizing antibody-antigen interactions, studying receptor-ligand dynamics, and probing structural changes within large protein complexes.
Synthesis and Implementation
Incorporation into Peptide Sequences
The integration of the Abz group into peptides is achieved through standard solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) protocols. Special Fmoc-protected Abz derivatives are commercially available and function like standard amino acids during the synthesis cycle. This allows for precise, site-specific incorporation at the N-terminus, the C-terminus, or even at internal positions within the peptide chain, providing immense flexibility in probe design. Specialized service providers, such as LifeTein, offer custom peptide synthesis with Abz and various quenchers, enabling researchers to obtain high-purity, assay-ready substrates without the need for in-house synthetic expertise.
Designing an Effective Substrate
Creating an optimal Abz-labeled substrate requires careful consideration:
- Selection of Quencher: The quencher must have a strong spectral overlap with Abz’s emission. Dnp and Tyr(NO2) are classic, effective, and economical choices.
- Cleavage Sequence: The peptide linker must contain the specific recognition and cleavage sequence for the target enzyme.
- Length and Flexibility: The peptide must be long enough to allow efficient FRET when intact but should not hinder enzyme access to the cleavage site.
Find out more about peptide synthesis here.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What does “Abz” stand for in peptide labeling?
Abz is the standard abbreviation for 2-aminobenzoyl, a fluorescent aromatic group derived from anthranilic acid. It functions as a highly efficient donor fluorophore in fluorescence-based assays.
How does an Abz/Dnp-labeled peptide work in a protease assay?
In an Abz/Dnp-labeled peptide, the Dnp group acts as a quencher for Abz fluorescence via FRET. When the intact peptide is excited, minimal fluorescence is detected. Upon cleavage by a specific protease between the two labels, they separate, FRET is abolished, and a strong increase in Abz fluorescence occurs, providing a direct measure of protease activity.
What are the main advantages of using Abz over other fluorophores like FAM or FITC?
Abz offers several key advantages: its larger Stokes shift reduces spectral interference, it is generally more photostable than fluorescein derivatives, and its excitation in the UV range can minimize background autofluorescence from biological samples, which is often excited at higher wavelengths.
Karaseva, M. A., Chukhontseva, K. N., Lemeskina, I. S., Pridatchenko, M. L., Kostrov, S. V., & Demidyuk, I. V. (2019). An Internally Quenched Fluorescent Peptide Substrate for Protealysin. Scientific Reports, 9(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-50764-2
Bernegger, S., Brunner, C., Vizovišek, M., Fonovic, M., Cuciniello, G., Giordano, F., Stanojlovic, V., Jarzab, M., Simister, P., Feller, S. M., Obermeyer, G., Posselt, G., Turk, B., Cabrele, C., Schneider, G., & Wessler, S. (2020). A novel FRET peptide assay reveals efficient Helicobacter pylori HtrA inhibition through zinc and copper binding. Scientific Reports, 10(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-67578-2