Peptides, short chains of amino acids, are fundamental in various biological processes and therapeutic applications. The incorporation of D-amino acids into peptides has garnered significant interest due to their unique properties and potential benefits. This article explores whether your peptides should include D-amino acids, focusing on their advantages, applications, and scientific considerations.
Key Takeaways:
- D-amino acids can enhance the stability and bioavailability of peptides.
- They are less susceptible to enzymatic degradation.
- D-peptides can have unique biological activities compared to their L-counterparts.
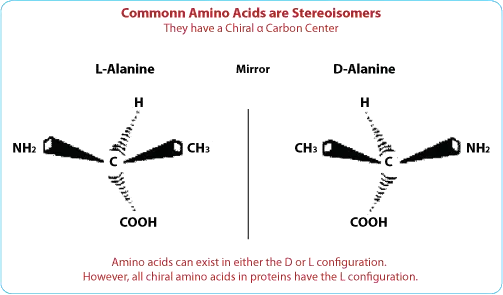
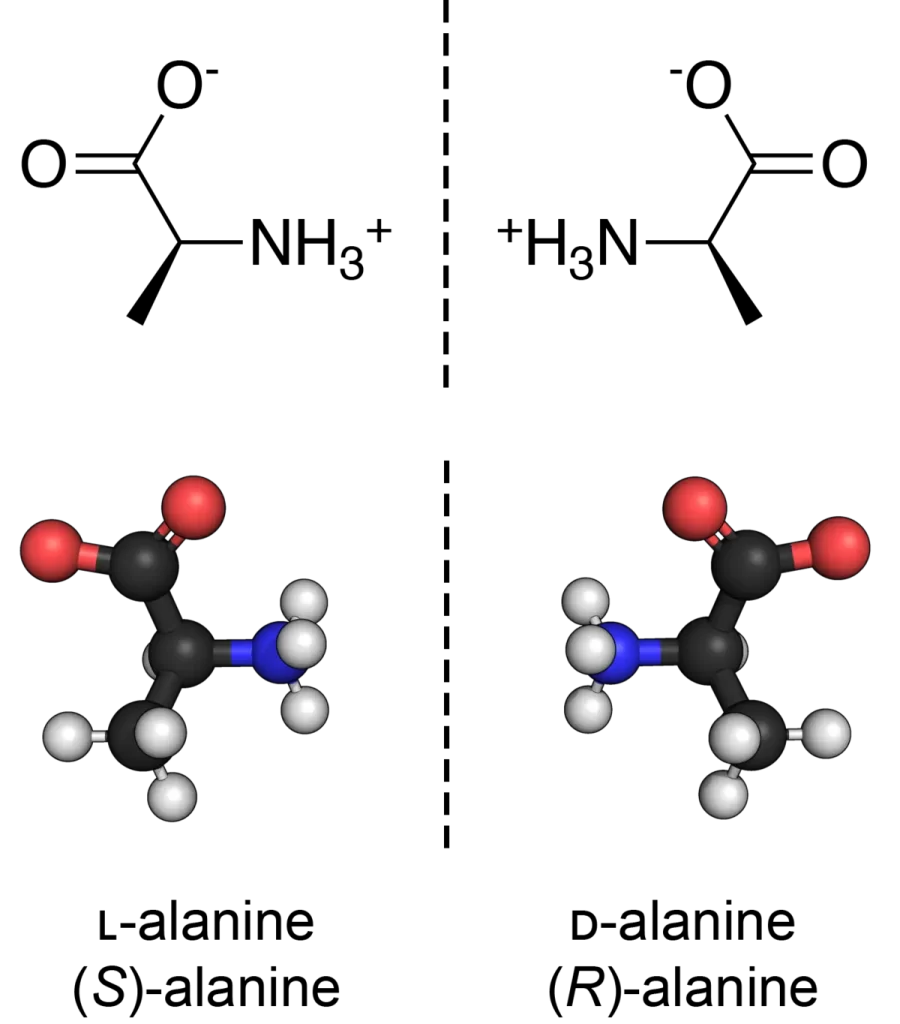
What Are D-Amino Acids?
Definition and Characteristics
D-amino acids are the mirror images of the more common L-amino acids. While L-amino acids are predominantly found in nature and are the building blocks of proteins, D-amino acids are less common but possess unique properties that can be advantageous in peptide design.
Natural Occurrence
D-amino acids are naturally present in some bacterial cell walls and certain peptides in higher organisms. Their presence in these contexts suggests they play specific biological roles that differ from those of L-amino acids.
Benefits of Incorporating D-Amino Acids in Peptides
Enhanced Stability
One of the primary benefits of incorporating D-amino acids into peptides is their enhanced stability. Peptides containing D-amino acids are more resistant to enzymatic degradation, which can significantly increase their half-life in biological systems.
Improved Bioavailability
D-peptides often exhibit improved bioavailability compared to their L-counterparts. This means they can be more effectively absorbed and utilized by the body, making them particularly useful in therapeutic applications.
Unique Biological Activities
D-peptides can exhibit unique biological activities that are not observed in peptides composed solely of L-amino acids. This can include increased binding affinity to certain receptors or enhanced antimicrobial properties.
Find out more about peptide synthesis here.
Applications of D-Peptides
Therapeutic Uses
D-peptides are being explored for various therapeutic applications, including as antimicrobial agents, enzyme inhibitors, and hormone analogs. Their resistance to degradation makes them ideal candidates for drugs that require prolonged activity.
Research Tools
In research, D-peptides are valuable tools for studying protein-protein interactions and for developing protease-resistant probes. Their unique properties allow scientists to investigate biological processes that are not accessible with traditional L-peptides.
Mechanisms of Enhanced Stability
Resistance to Enzymatic Degradation
One of the key mechanisms by which D-amino acids enhance peptide stability is their resistance to enzymatic degradation. Enzymes that typically break down peptides, such as proteases, are less effective against D-peptides due to the different spatial configuration of D-amino acids. This resistance allows D-peptides to maintain their structure and function for longer periods in biological environments.
Structural Rigidity
D-amino acids can also contribute to the structural rigidity of peptides. This rigidity can prevent the peptide from adopting conformations that are susceptible to enzymatic attack, further enhancing stability. The increased rigidity can also improve the binding affinity of the peptide to its target, enhancing its biological activity.
Read more about our D-Peptides here.
Case Studies of D-Peptides
Antimicrobial D-Peptides
D-peptides have shown promise as antimicrobial agents. For example, certain D-peptides have been designed to target bacterial membranes, disrupting their integrity and leading to bacterial cell death. These D-peptides are not only effective but also less likely to be degraded by bacterial enzymes, making them potent antimicrobial agents.
Enzyme Inhibitors
Another application of D-peptides is in the development of enzyme inhibitors. D-peptides can be designed to bind to the active sites of enzymes, blocking their activity. Due to their resistance to degradation, these inhibitors can remain active for longer periods, providing sustained therapeutic effects.
Future Directions
Personalized Medicine
The use of D-peptides in personalized medicine is an exciting area of research. By tailoring D-peptides to the specific needs of individual patients, it may be possible to develop highly effective treatments with minimal side effects. This approach could revolutionize the way we treat diseases, offering more precise and targeted therapies.
Drug Delivery Systems
D-peptides are also being explored as components of drug delivery systems. Their stability and bioavailability make them ideal candidates for delivering drugs to specific tissues or cells. By incorporating D-peptides into drug delivery vehicles, it may be possible to enhance the efficacy and safety of various therapeutic agents.
FAQ
What are D-amino acids?
D-amino acids are the mirror images of the more common L-amino acids. They have unique properties that can enhance the stability and bioavailability of peptides.
Why are D-peptides more stable than L-peptides?
D-peptides are more stable because they are less susceptible to enzymatic degradation. The different spatial configuration of D-amino acids makes it harder for enzymes to break them down.
What are some applications of D-peptides?
D-peptides are used in various applications, including as antimicrobial agents, enzyme inhibitors, and components of drug delivery systems. They are also valuable tools in research for studying protein-protein interactions.
Are there any drawbacks to using D-amino acids in peptides?
While D-amino acids offer many advantages, they can be more challenging to synthesize and may have different biological activities compared to L-amino acids. It is important to carefully consider these factors when designing D-peptides.