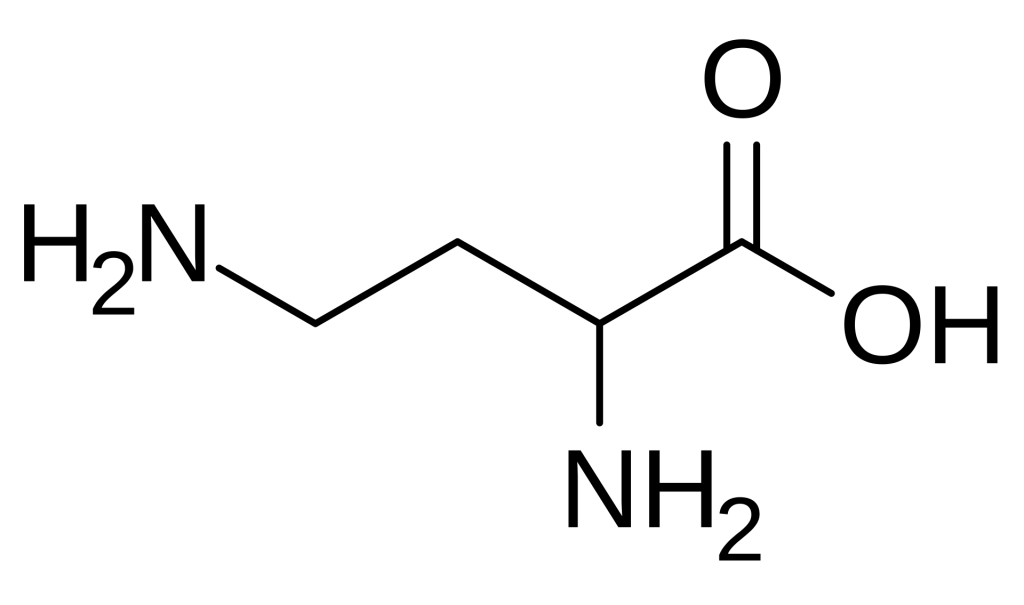
2,4-Diaminobutyric acid (Dab) is a fascinating non-proteinogenic diamino acid that has garnered significant attention in peptide chemistry and biomedical research. Structurally characterized by the presence of two amino groups at the alpha and gamma positions of a four-carbon backbone, this unusual amino acid serves as a versatile building block for creating peptides with unique structural and functional properties. Unlike standard amino acids encoded by the genetic code, Dab must be incorporated into peptides through specialized synthetic strategies, making it a valuable tool for researchers seeking to introduce additional charge, hydrogen-bonding capacity, or conformational constraints into their peptide sequences. Its biological significance extends beyond synthetic utility, as Dab occurs naturally in various organisms and exhibits interesting pharmacological activities, including interactions with neurotransmitter systems and potential anticancer properties.
Key Takeaways
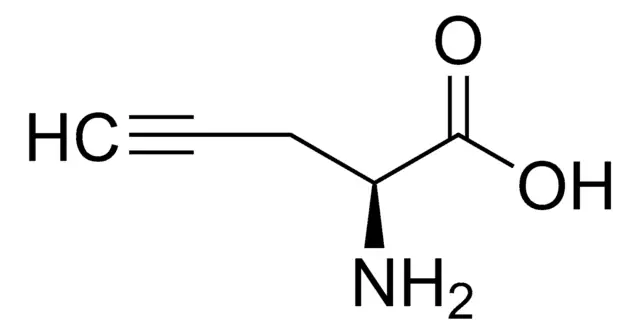
- 2,4-Diaminobutyric acid (Dab) is a non-proteinogenic diamino acid with the molecular formula C4H10N2O2 and a structure featuring amino groups at both the 2-position (alpha) and 4-position (gamma) of the butyric acid backbone.
- Dab exists as two stereoisomers, L-Dab and D-Dab, which exhibit markedly different biological activities. The S(+) isomer is at least 20 times more potent than the R(-) isomer at inhibiting GABA uptake in neuronal tissues.
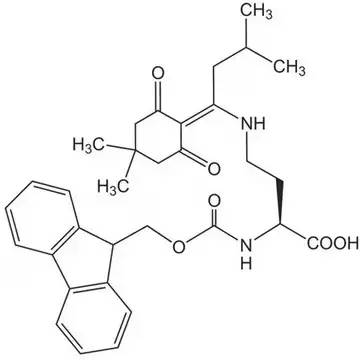
- In peptide synthesis, Dab requires orthogonal protecting group strategies, commonly using derivatives like Dde-Dab(Fmoc)-OH, to enable selective deprotection and site-specific functionalization during solid-phase peptide synthesis.
- Dab-containing peptides have demonstrated antitumoral activity against human glioma cells, attributed to concentrated uptake leading to osmotic cellular lysis.
- The incorporation of Dab into cyclic dipeptides enables the formation of conformationally constrained structures, such as 5-membered lactam rings, which are valuable for studying protein structure-function relationships.
Chemical Fundamentals of 2,4-Diaminobutyric Acid
Definition and Structural Characteristics of Dab
2,4-Diaminobutyric acid is formally defined as a diamino acid derived from butyric acid, wherein hydrogen atoms at positions 2 and 4 are replaced by amino groups. Its molecular formula is C4H10N2O2, with an average mass of 118.13 g/mol. The compound features an alpha amino group adjacent to the carboxylic acid and a gamma amino group at the end of the aliphatic chain, creating a structure with two positively charged centers at physiological pH. This dual cationic character distinguishes Dab from standard amino acids and imparts unique physicochemical properties, including enhanced water solubility and the ability to participate in multiple hydrogen-bonding interactions.
Isomeric Forms and Stereochemistry
A critical aspect of Dab chemistry is its existence as two distinct stereoisomers due to the chiral center at the alpha carbon. The L-isomer (S-configuration) and D-isomer (R-configuration) exhibit profound differences in their biological activities. Research has demonstrated that S(+)-2,4-diaminobutyric acid is approximately 20 times more potent than the R(-) stereoisomer as an inhibitor of sodium-dependent GABA uptake in rat brain slices. Interestingly, both isomers display equipotent inhibition of sodium-independent GABA binding to brain membranes, suggesting that the stereospecificity relates specifically to transporter interactions rather than receptor binding. This stereochemical discrimination underscores the importance of using the correct isomer when designing Dab-containing peptides for neurobiological applications.
Find out more about peptide synthesis here.
Dab Applications in Peptide Synthesis
Orthogonal Protection Strategies
The incorporation of Dab into synthetic peptides presents unique challenges due to the presence of two reactive amino groups that must be differentially protected during solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS). Commercial suppliers offer specialized derivatives such as Dde-Dab(Fmoc)-OH (CAS 1263045-85-7), which features both Dde and Fmoc protecting groups. This orthogonal protection scheme allows for selective deprotection of the N-terminal Fmoc group during chain assembly while maintaining the Dde protection on the side chain amino group. Consequently, researchers can achieve site-specific functionalization of the Dab residue after peptide synthesis is complete, enabling the creation of branched peptides, cyclic structures, or conjugates with fluorophores or other probes.
Formation of Conformationally Constrained Peptides
Dab serves as an exceptional building block for introducing conformational constraints into peptide structures. When incorporated into peptide sequences, the gamma amino group can participate in cyclization reactions to form 5-membered lactam rings. Research has demonstrated that Boc derivatives of 2,4-diaminobutyric acid can be used to synthesize cyclic dipeptides that serve as substrates for incorporation into proteins using modified ribosomal systems. These conformationally constrained analogues provide valuable tools for studying protein folding, enzyme-substrate interactions, and the structural requirements for biological activity. The ability to lock peptides into specific conformations through Dab-mediated cyclization has important implications for drug discovery and the development of peptide-based therapeutics.
Biological Significance and Pharmacological Activity of Dab
Interaction with GABAergic Systems
One of the most extensively studied biological activities of Dab relates to its interaction with the GABA neurotransmitter system. As a structural analogue of gamma-aminobutyric acid, Dab acts as an inhibitor of sodium-dependent GABA uptake in neuronal tissues. This property has made Dab-containing peptides valuable pharmacological tools for investigating GABAergic neurotransmission and developing potential therapeutic agents for neurological disorders. The stereospecificity of this inhibition, with the S(+) isomer being substantially more potent, highlights the importance of chiral purity in Dab-based research compounds.
Anticancer Properties
Emerging evidence suggests that Dab possesses antitumoral activity, particularly against glioma cells. The compound is transported into cells by the System A amino acid transporter, and its concentrated uptake in glioma cells can lead to osmotic lysis. This mechanism exploits the enhanced metabolic demands of cancer cells and their increased expression of amino acid transporters. The potential for Dab to serve as a selective anticancer agent, especially against brain tumors, represents an exciting avenue for therapeutic development. Researchers exploring this application rely on custom peptide synthesis services to create Dab-containing compounds with optimized pharmacokinetic properties.
Find out about high-speed RUSH synthesis.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between 2,4-diaminobutyric acid and ornithine?
Both are diamino acids, but they differ in chain length. 2,4-Diaminobutyric acid (Dab) has a four-carbon backbone with amino groups at positions 2 and 4, whereas ornithine has a five-carbon backbone with amino groups at positions 2 and 5. This structural difference affects the ring size when forming cyclic derivatives. Dab forms 5-membered lactams, while ornithine forms 6-membered rings.
Why is orthogonal protection necessary for Dab in peptide synthesis?
Dab contains two chemically similar amino groups that must be selectively deprotected during SPPS. Orthogonal protecting groups like Dde and Fmoc allow researchers to remove one protecting group without affecting the other, enabling precise control over where modifications occur. This is essential for creating branched peptides, cyclic structures, or site-specifically labeled conjugates.
Can Dab be incorporated into peptides for therapeutic applications?
Yes, Dab-containing peptides have shown promise in various therapeutic contexts, particularly as anticancer agents targeting glioma cells and as pharmacological tools for studying GABAergic neurotransmission. However, researchers must carefully consider the stereoisomer used, as biological activity differs dramatically between L- and D-forms.
How does Dab affect peptide conformation?
The dual amino groups of Dab enable the formation of intramolecular lactam bridges, creating conformationally constrained cyclic peptides. These constraints can stabilize specific secondary structures, such as turns or helices, and provide insights into the bioactive conformations required for target interactions.
JOHNSTON, G. A. R., & TWITCHIN, B. (1977). STEREOSPECIFICITY OF 2,4‐DIAMINOBUTYRIC ACID WITH RESPECT TO INHIBITION OF 4‐AMINOBUTYRIC ACID UPTAKE AND BINDING. British Journal of Pharmacology, 59(1), 218–219. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb06998.x
Zhang, C., Bai, X., Dedkova, L. M., & Hecht, S. M. (2020). Protein synthesis with conformationally constrained cyclic dipeptides. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 28(22), 115780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115780
Batoon, P., & Ren, J. (2015). Proton affinity of dipeptides containing alanine and diaminobutyric acid. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 378, 151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijms.2014.07.025