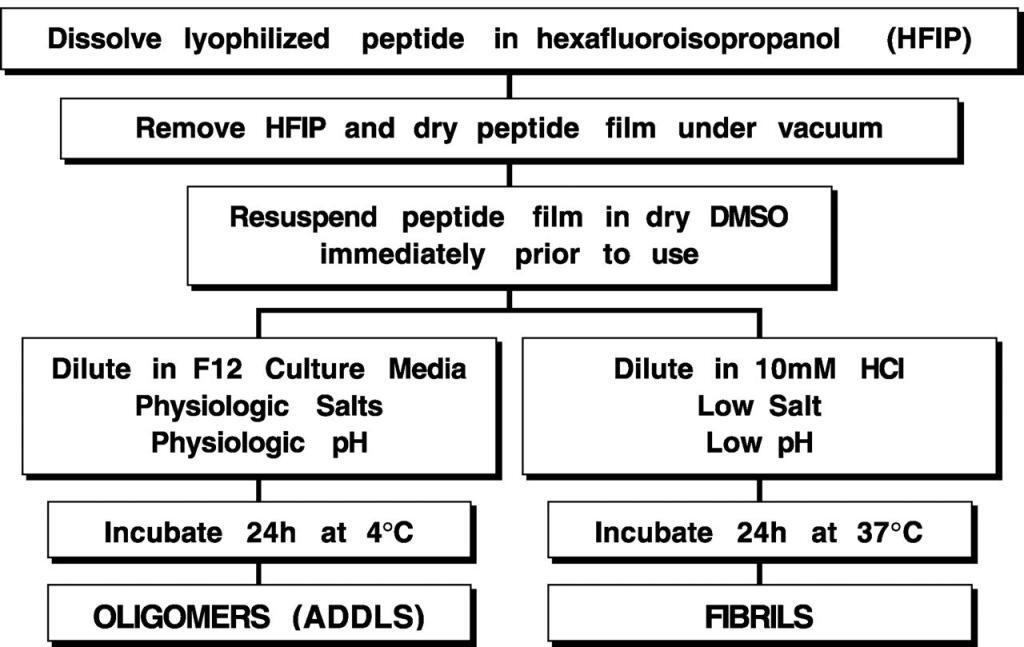
Aβ-(1–42) was dissolved to 1 mM in 100% hexafluoroisopropanol, hexafluoroisopropanol was removed under vacuum, and the peptide was stored at −20 °C. For the aggregation protocols, the peptide was first resuspended in dry Me2SO (DMSO) to 5 mM. For oligomeric conditions, F-12 (without phenol red) culture media was added to bring the peptide to a final concentration of 100 μM, and the peptide was incubated at 4 °C for 24 h. For fibrillar conditions, 10 mM HCl was added to bring the peptide to a final concentration of 100 μM, and the peptide was incubated for 24 h at 37 °C.
ADDLS, amyloid-derived diffusible ligands.
Preparing human islet amyloid polypeptide (hIAPP), also known as amylin, can be challenging due to its hydrophobic amino acid residues.
Here’s an improved method for dissolving lyophilized hIAPP:
- Begin by dissolving lyophilized hIAPP in 80% (v/v) HFIP containing 10 mM HCl. This step ensures complete dissolution. The CD spectrum indicates the presence of a stable alpha-helical conformation, which remains so for several days.
- Next, remove the HFIP by lyophilization, leaving behind lyophilized hIAPP.
- Re-dissolve the lyophilized hIAPP in 10 mM HCl, and eliminate any insoluble components by ultracentrifugation.
- The resulting hIAPP solution in 10 mM HCl is ready for immediate use in experiments.
To initiate the formation of hIAPP fibrils, introduce the stock solution into the reaction buffer. Conditions for fibril formation were optimized under two pH conditions:
- Low pH: Utilize 25 uM hIAPP in 10 mM HCl, with varying concentrations of HFIP.
- Neutral pH: Employ 25 uM hIAPP in a 50 mM sodium phosphate buffer at pH 7.0, with varying concentrations of HFIP.
Incubate these samples at 25 °C for several hours.
Reference: JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY 23965, JULY 8, 2011 VOLUME 286 NUMBER 27
Aducanumab is a human monoclonal antibody that has been studied for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease.
