
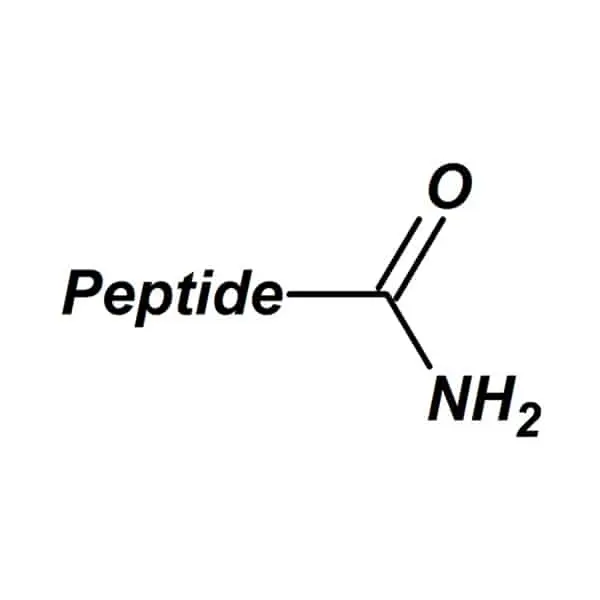
C-terminal amidation is a critical post-translational modification where the carboxylic acid group (-COOH) at a peptide’s C-terminus is converted to an amide group (-CONH₂). This seemingly minor chemical change profoundly impacts a peptide’s biological activity, receptor binding affinity, and metabolic stability. Researchers designing therapeutic peptides or biochemical probes must carefully weigh structural, functional, and physiological factors when deciding whether to be amidated.
Key Takeaways
- C-terminal amidation neutralizes negative charge, enhancing receptor binding for most bioactive peptides.
- Over 50% of peptide hormones (e.g., neuropeptide Y, oxytocin) occur naturally in amidated form.
- Amidation improves proteolytic resistance by 30–60% compared to acidic forms.
- Non-amidated peptides exhibit higher polarity, significantly reducing cellular permeability.
- Synthesis requires specialized resins (e.g., Rink amide) or solution-phase modification.
Fundamentals of Peptide Amidation
Chemical Basis and Biological Prevalence
C-terminal amidation replaces the terminal carboxyl group with a carboxamide moiety, removing its acidic proton. This modification is enzymatically catalyzed in vivo by peptidylglycine α-amidating monooxygenase (PAM), which processes glycine-extended precursors into bioactive amidated peptides. Approximately 60% of neuropeptides undergo this modification, highlighting its physiological importance. Eliminating the negative charge induces conformational changes that optimize receptor-ligand interactions by reducing electrostatic repulsion.
Functional Consequences of Amidation
Enhanced Biological Activity
For peptides like neuropeptides, hormones, and antimicrobial peptides, amidation dramatically boosts efficacy. This results from structural stabilization of bioactive conformations and improved membrane interactions.
Improved Metabolic Stability
Amidation confers resistance to carboxypeptidases by eliminating the charged C-terminal recognition site. Reduced polarity also decreases renal clearance, extending systemic exposure.
Influence on Solubility and Aggregation
Charge neutralization increases hydrophobicity, which may reduce aqueous solubility but enhance membrane permeability—critical for CNS-targeting peptides crossing the blood-brain barrier. However, heightened hydrophobicity can increase aggregation propensity, requiring formulation adjustments.
Decision Framework for Amidation
Native Sequence Mimicry
Always replicate endogenous modifications when studying physiological systems. If the native peptide is amidated (e.g., substance P, vasoactive intestinal peptide), synthetic versions must match this to ensure bioequivalence.
Functional Domain Considerations
Evaluate the peptide’s active site topology: Amidation is essential if receptor binding involves C-terminal residues (e.g., opioid peptides). N-terminally active peptides (e.g., angiotensin) may tolerate C-terminal modifications. Computational modeling or alanine scanning data can guide this decision.
Physicochemical Optimization
For engineered peptides:
- Amidate to boost proteolytic stability and membrane permeation.
- Retain carboxylate to improve solubility or enable conjugation chemistry.
- Consider alternative modifications (e.g., esterification) for intermediate properties.
Synthesis and Characterization
Solid-Phase Synthesis Protocols
Amidated peptides require amide-functionalized resins (e.g., Rink amide MBHA resin) during Fmoc/tBu SPPS. Cleavage automatically generates the C-terminal amide. For solution-phase synthesis, use carbodiimide-mediated amidation with ammonium salts.
Analytical Verification
Confirm amidation via:
- Mass spectrometry: +0.984 Da mass shift vs. carboxylic acid form.
- Isoelectric focusing: Higher pI due to charge elimination.
- Reversed-phase HPLC: Increased retention time reflecting hydrophobicity.
Find out about high-speed RUSH synthesis.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Does amidation affect peptide immunogenicity?
Generally no. Antibody recognition depends on epitope conformation, not C-terminal charge. Exceptions exist for antibodies targeting extreme C-termini.
How does amidation cost compare to standard synthesis?
LifeTein can provide amindation at no additional cost to the synthesis.
Is amidation reversible in biological systems?
No. Unlike acetylation or phosphorylation, amidation is a permanent modification with no known mammalian reversal enzymes.
