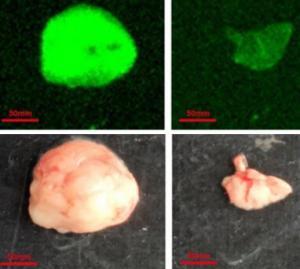
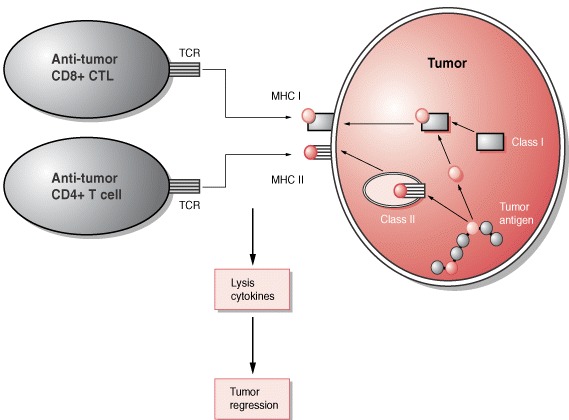
Cancer is a patient-specific disease, where no two tumors are alike. Neoepitopes are very frequent in all cancers. Amino acid substitutions can yield neoantigens that are detected by the immune system. So neoantigens have been used for therapeutic purposes such as identifying cancer variant peptides for diagnosis and treatment.
The
1. The 9-
2. The
3. Only a minority of predicted neoepitopes elicit protective tumor immunity. Peptide binding to a Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) molecule is a requirement for raising adaptive immunity.
How should we immunize against neoepitopes?
Since neoantigens are small peptides harboring tumor mutations, immunization with them usually needs strong immunostimulatory agents to produce an effective immune response.
Peptides as vaccines may not be able to stimulate the immune system powerfully enough on their own. Therefore, it is usually required to use an adjuvant in combination to elicit an effective immune response.
However, the MAPs-4 system, in which four copies of the same peptide epitope are synthesized on a lysine-based core, does not require a carrier protein, as the dense packing of multiple copies of an epitope in combination with a high-molar ratio produces a robust immunological response.
Accurate identification of neoepitopes and their subsequent use in cancer therapy is still in its nascent stages. With recent advances in Mass Spectrometry, faster and more precise identification of all expressed neoepitopes may be possible soon.
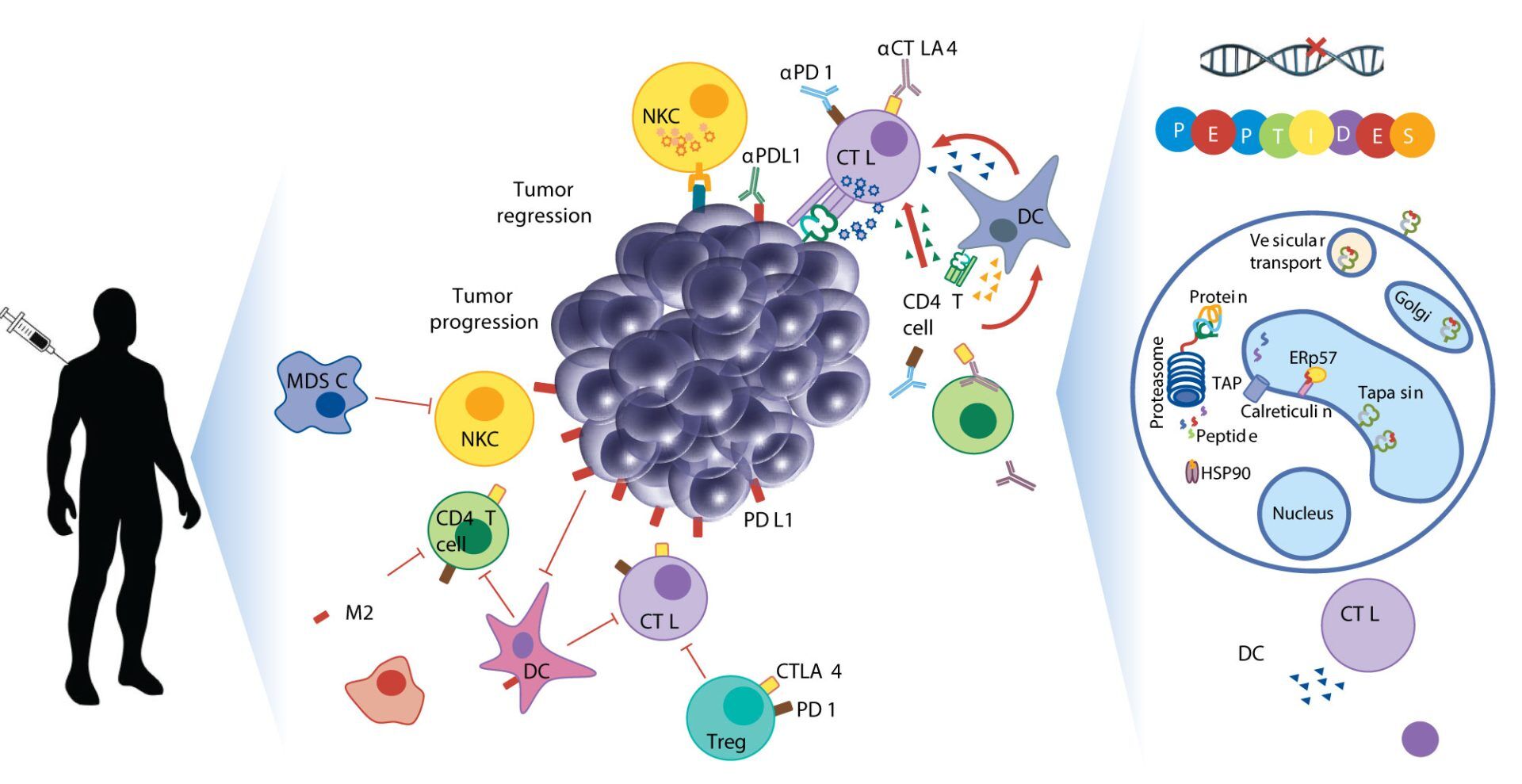
Neoepitopes as cancer immunotherapy targets: key challenges and opportunities