Stapled peptides represent a significant advancement in the field of therapeutic peptides, offering enhanced stability, specificity, and cellular uptake compared to their linear counterparts. This innovative approach to peptide design has opened new avenues in drug development, particularly in targeting intracellular protein-protein interactions that were previously considered undruggable.
Key Takeaways:
- Stapled peptides are chemically modified to lock them in an alpha-helical conformation, enhancing their bioavailability and efficacy.
- They exhibit increased resistance to proteolytic degradation, extending their half-life in biological systems.
- These peptides have shown promise in targeting challenging pathways involved in cancer, infectious diseases, and other conditions.
Introduction to Stapled Peptides
What are Stapled Peptides?
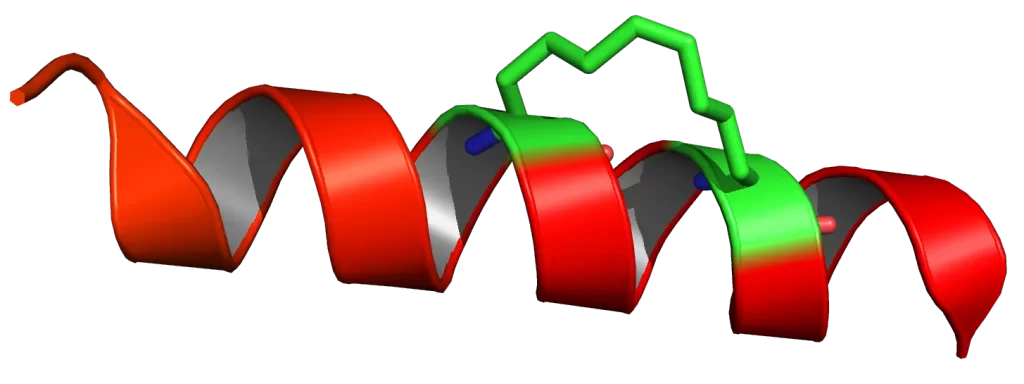
Stapled peptides are a class of synthetic peptides whose structure includes a chemical “staple” that locks the peptide in a specific conformation. This stapling typically enforces an alpha-helical structure, which is crucial for the interaction with many intracellular targets.
The Stapling Process
The process involves the covalent linkage of two non-adjacent amino acids within the peptide chain, often through a hydrocarbon bridge. This modification stabilizes the helical structure and enhances the peptide’s overall pharmacological properties.
Advantages of Stapled Peptides

Enhanced Stability and Half-life
By resisting enzymatic degradation, stapled peptides maintain their integrity and function longer in the biological environment, offering an extended therapeutic window.
Improved Cellular Uptake
The alpha-helical structure facilitated by stapling promotes better penetration across cell membranes, allowing these peptides to reach intracellular targets effectively.
Specificity and Efficacy
Stapled peptides can be designed to closely mimic natural protein interactions, providing high specificity for their targets and reducing off-target effects.
For more information on peptide modifications, visit LifeTein’s peptide synthesis services.
Applications of Stapled Peptides
Cancer Therapy
Stapled peptides have been explored for their potential to modulate critical protein-protein interactions in cancer pathways, offering a new strategy for targeted therapy.
Infectious Diseases
Their ability to disrupt viral proteins and other pathogenic factors makes stapled peptides promising agents in treating infectious diseases.
Explore the potential of stapled peptides in drug development at LifeTein’s peptide library synthesis page.
Neurodegenerative Disorders
The unique properties of stapled peptides allow for the targeting of neurodegenerative disease pathways, including those involved in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How do stapled peptides differ from traditional peptides?
- Stapled peptides are chemically modified to maintain a specific conformation, enhancing their stability, cellular uptake, and target specificity.
- Can stapled peptides be used for all types of diseases?
- While promising, stapled peptides’ applicability depends on the nature of the disease and the target pathway. They are most effective in conditions where targeting protein-protein interactions is beneficial.
- What are the main challenges in developing stapled peptide therapies?
- Challenges include the complexity of synthesis, ensuring effective delivery to the target site, and achieving selective and potent interaction with the target protein.
