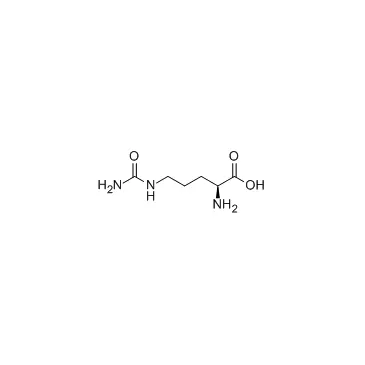
Citrulline, an unnatural amino acid, is a non-proteinogenic amino acid that plays a significant role in the urea cycle and nitric oxide production. Unlike proteinogenic amino acids, citrulline is not directly encoded by DNA but is synthesized through metabolic pathways. This article explores the properties, synthesis, and applications of citrulline, with insights from LifeTein’s expertise in custom peptide synthesis.
Key Takeaways
- Non-Proteinogenic Amino Acid: Citrulline is not encoded by DNA but plays a crucial role in the urea cycle.
- Metabolic Intermediate: Acts as an intermediate in the urea cycle, converting ammonia into urea.
- Nitric Oxide Production: Involved in the production of nitric oxide, which helps in vasodilation.
- LifeTein Expertise: LifeTein offers custom synthesis of citrulline-containing peptides for research purposes.
Properties of Citrulline
Chemical Structure
Citrulline, also known as 2-amino-5-(carbamoylamino)pentanoic acid, has a molecular formula of C6H13N3O3. It is a white crystalline powder that is soluble in water.
Role in the Urea Cycle
Citrulline is a key intermediate in the urea cycle, which is the primary pathway for the removal of ammonia in mammals. The cycle converts toxic ammonia into urea, which is then excreted in urine.
Nitric Oxide Production
Citrulline is also involved in the production of nitric oxide (NO), a molecule that plays a crucial role in vasodilation and blood flow regulation. The conversion of citrulline to arginine, catalyzed by nitric oxide synthase (NOS), is a critical step in NO production.
Synthesis of Citrulline
Biosynthesis
Citrulline is synthesized from ornithine and carbamoyl phosphate in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme ornithine transcarbamylase. This reaction is a central step in the urea cycle.
Chemical Synthesis
Citrulline can also be synthesized chemically through various methods, including the reaction of asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) with dimethylarginine deiminase (DDAH). This synthetic approach is used for producing citrulline for research and therapeutic purposes.
Find more peptide synthesis here
Applications of Citrulline
Medical and Therapeutic Uses
Citrulline is used in medical research to study metabolic disorders and cardiovascular diseases. Its role in the urea cycle makes it a potential therapeutic agent for conditions related to ammonia toxicity.
Sports and Exercise
Citrulline is popular among athletes and bodybuilders due to its potential to enhance blood flow and improve exercise performance. Supplements containing citrulline are marketed for their ability to boost nitric oxide production and reduce muscle fatigue.
Research Applications
LifeTein offers custom peptide synthesis services, including the incorporation of citrulline into peptides for research purposes. Researchers can utilize citrulline-containing peptides to study various biological processes and develop new therapeutic strategies.
Find our expedited synthesis service here
Future Directions
Advancements in Synthesis Techniques
Ongoing research aims to develop more efficient and scalable methods for synthesizing citrulline and its derivatives. Innovations in chemical synthesis and biotechnological approaches are expected to enhance the availability and utility of citrulline in scientific research and therapeutics.
Expanding Applications
As the understanding of citrulline’s properties and applications grows, its use in various fields, including drug discovery and protein engineering, is likely to expand. LifeTein’s commitment to providing high-quality custom peptides will continue to support advancements in these areas.
FAQ
What Is Citrulline?
Citrulline is an unnatural amino acid that plays a crucial role in the urea cycle and nitric oxide production.
Why Is Citrulline Important?
Citrulline is important for its role in ammonia detoxification and nitric oxide production, which are essential for metabolic and cardiovascular health.
