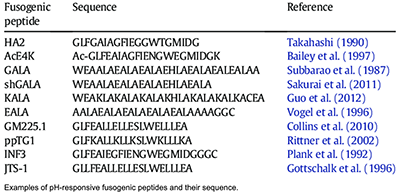
KALA Amphipathic Peptide (sequence: WEAKLAKALAKALAKHLAKALAKALKACEA) is a cationic, low-molecular weight amphipathic peptide with significant applications in biological research and drug delivery. This synthetic peptide is particularly noted for its ability to bind DNA, destabilize cellular membranes, and mediate the transfection of plasmid DNA into various cell lines.
Applications in Research and Drug Delivery
KALA peptide assumes an alpha-helical structure at physiological pH (around 7.5), which enhances its interaction with DNA and cell membranes. This makes it a powerful tool in gene therapy and drug delivery research, where it can be used to deliver genetic material into cells with high efficiency. The peptide’s ability to disrupt membranes is crucial for overcoming cellular barriers, thereby facilitating the entry of therapeutic agents.
In addition to its role in DNA delivery, KALA is also a starting point for developing a family of peptides designed to improve the efficiency and specificity of drug delivery systems. Its cationic nature enables the condensation of plasmid DNA, a critical step in many gene therapy applications.
Molecular Details
The peptide has a molecular formula of C???H???N??O??S and a molecular weight of 3131.87 g/mol. It is generally stored at temperatures below -15°C to maintain its stability. Given its versatility and effectiveness, KALA peptide is widely used in research focused on enhancing gene delivery and exploring novel therapeutic approaches.
Researchers working on gene therapy, drug delivery, or membrane biology will find KALA amphipathic peptide to be an essential tool for advancing their studies and developing new therapeutic strategies. |