|
The acpP-targeting antisense PNA CTCATACTCT, particularly when linked to the cell wall/membrane-active peptide KFFKFFKFFK, demonstrated a remarkable increase in antisense efficacy in E. coli, up to a hundredfold, while maintaining their target specificity.
The Peptide-PNA Conjugate represents a novel class of antimicrobial agents designed to combat multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria. This conjugate combines the unique properties of peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) with a specialized peptide sequence to enhance bacterial uptake and antisense activity.
Key Features:
-
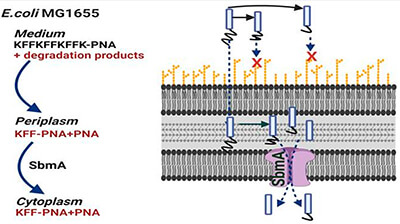
Structure and Composition: The conjugate consists of a linear, cationic peptide sequence (KFFKFFKFFK) covalently attached to a PNA oligomer with the sequence {CTCATACTCT}-NH2. This design leverages the envelope-disrupting properties of cationic bacteria penetrating peptides (BPPs).
-
Targeted Action Against MDR Bacteria: Specifically formulated to address the growing concern of antibiotic resistance, particularly in Gram-negative bacteria, which are resistant to many antibiotic classes.
-
Enhanced Bacterial Uptake: The cationic peptide component (KFFKFFKFFK) facilitates the translocation of the PNA across bacterial membranes, including the challenging multibarrier envelopes with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) layers.
-
Antisense Mechanism: The PNA component targets essential bacterial genes, capable of killing bacteria at low micromolar concentrations, offering a new avenue for antibiotic drug discovery.
-
SbmA Independent Activity: The conjugate's design allows for efficient crossing of the inner bacterial membrane without reliance on the SbmA transporter, overcoming a common resistance mechanism.
-
Stability and Metabolism Considerations: The peptide-PNA conjugate is designed with stability in mind, considering the susceptibility to degradation by bacterial proteases/peptidases.
Applications:
- Antibacterial Research: Ideal for studies focused on novel antibacterial agents, particularly against MDR bacteria.
- Drug Discovery: A promising candidate for the development of new antibiotics leveraging antisense technology.
- Mechanistic Studies: Useful in exploring the uptake processes and mode of action of antisense antibacterials.
Advantages:
- High Efficacy: Demonstrates potent antibacterial activity at low concentrations.
- Reduced Resistance Risk: Designed to circumvent common bacterial resistance mechanisms.
- Target Specificity: The PNA component allows for precise targeting of bacterial genes.
Considerations:
- Peptide Stability: The intact bacteria penetrating peptides (BPPs) are crucial for uptake but not for antisense activity, highlighting the importance of peptide stability in the bacterial environment.
- Mechanism of Action: Understanding the uptake and degradation processes is key to maximizing the efficacy of this conjugate.
The Peptide-PNA Conjugate (KFFKFFKFFK-{CTCATACTCT}-NH2) represents a cutting-edge approach in the fight against multidrug-resistant bacteria, offering a novel mechanism of action and enhanced efficacy. Its design and functionality make it a valuable tool for researchers and pharmaceutical developers aiming to address the critical challenge of antibiotic resistance.
Reference:
1. Niloofar Yavari, Lise Goltermann, and Peter E. Nielsen ACS Chemical Biology 2021 16 (3), 471-479 DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.0c00822
2. Good, L., Awasthi, S., Dryselius, R. et al. Bactericidal antisense effects of peptide–PNA conjugates. Nat Biotechnol 19, 360–364 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/86753
|